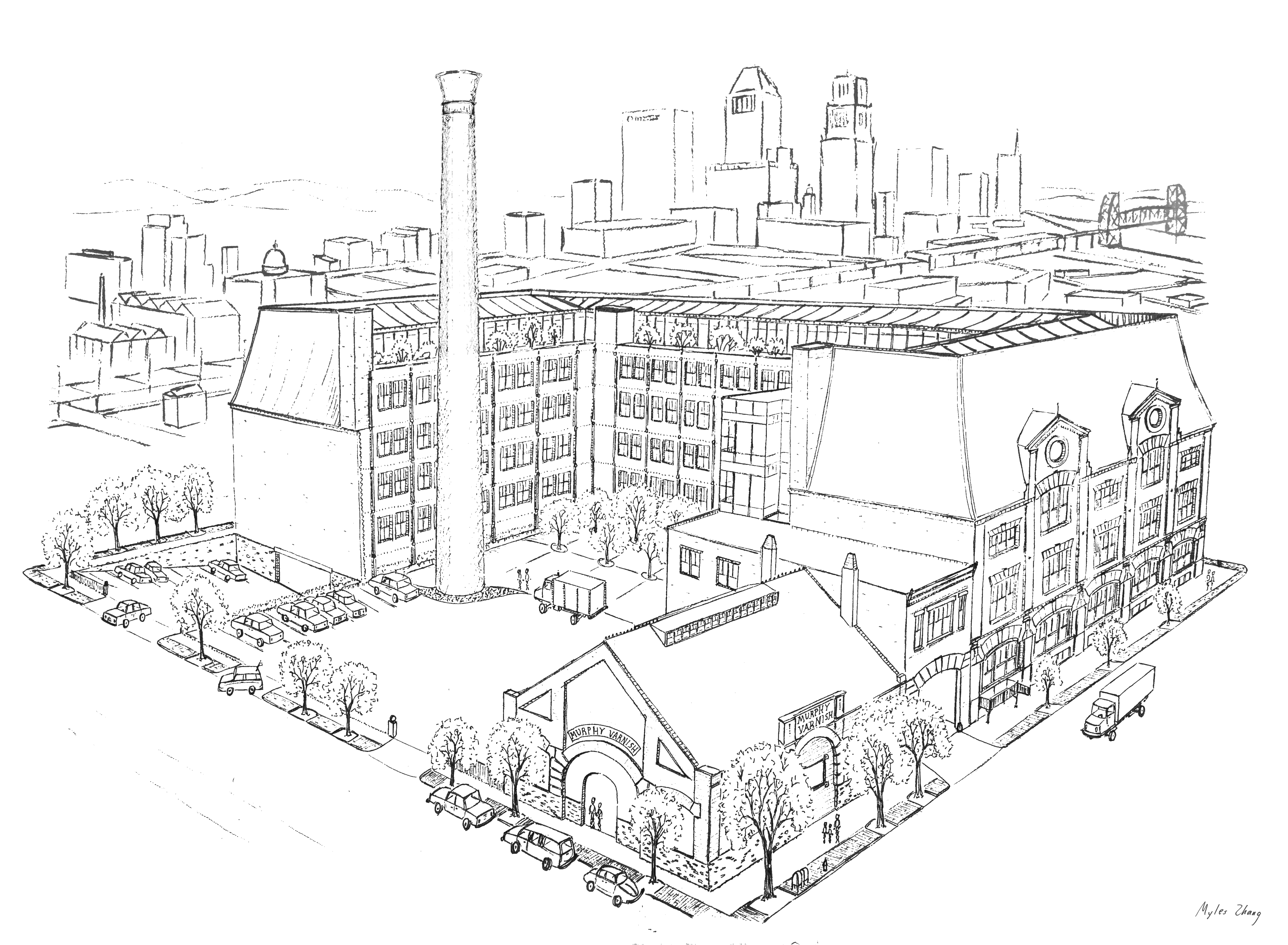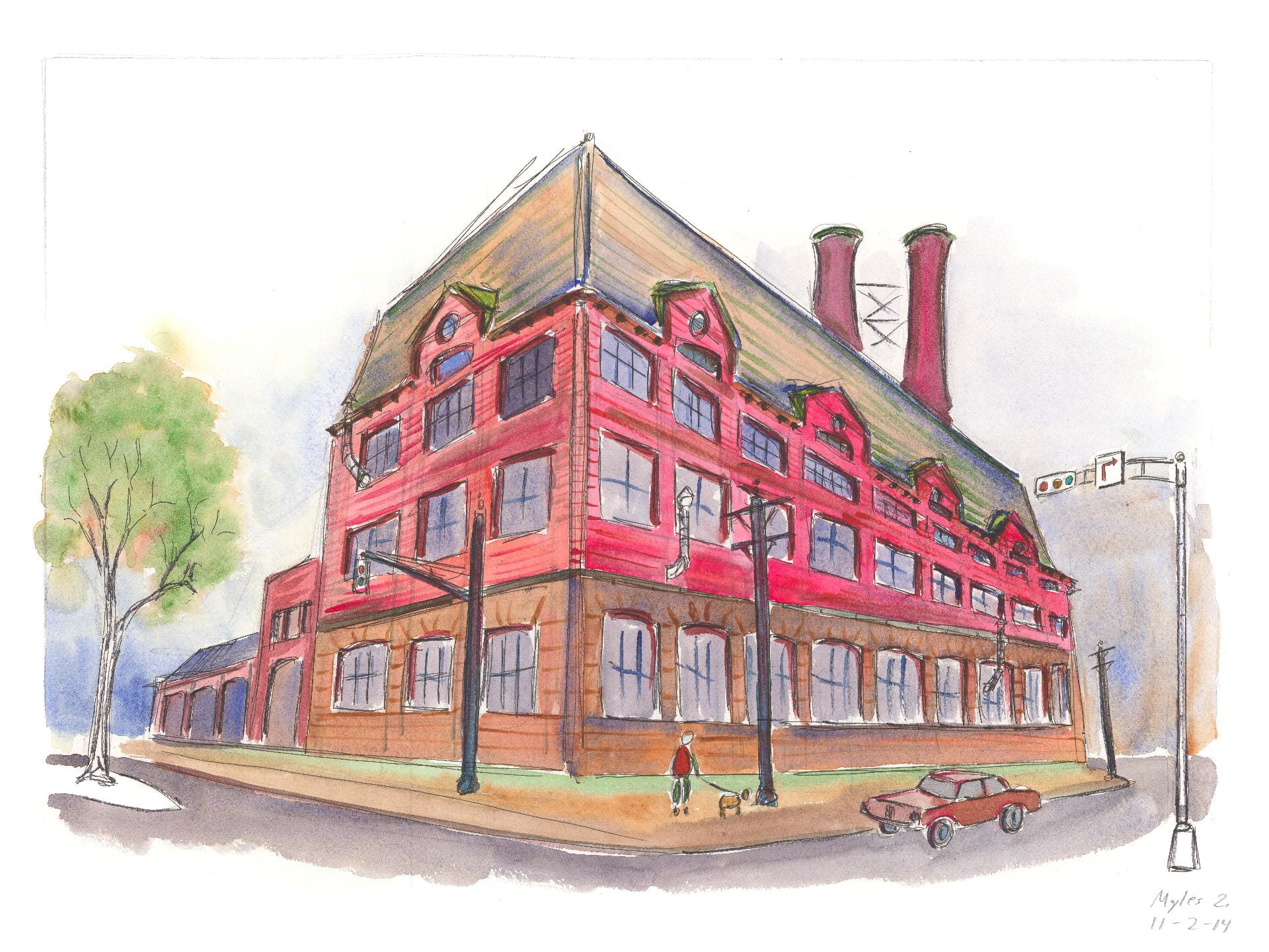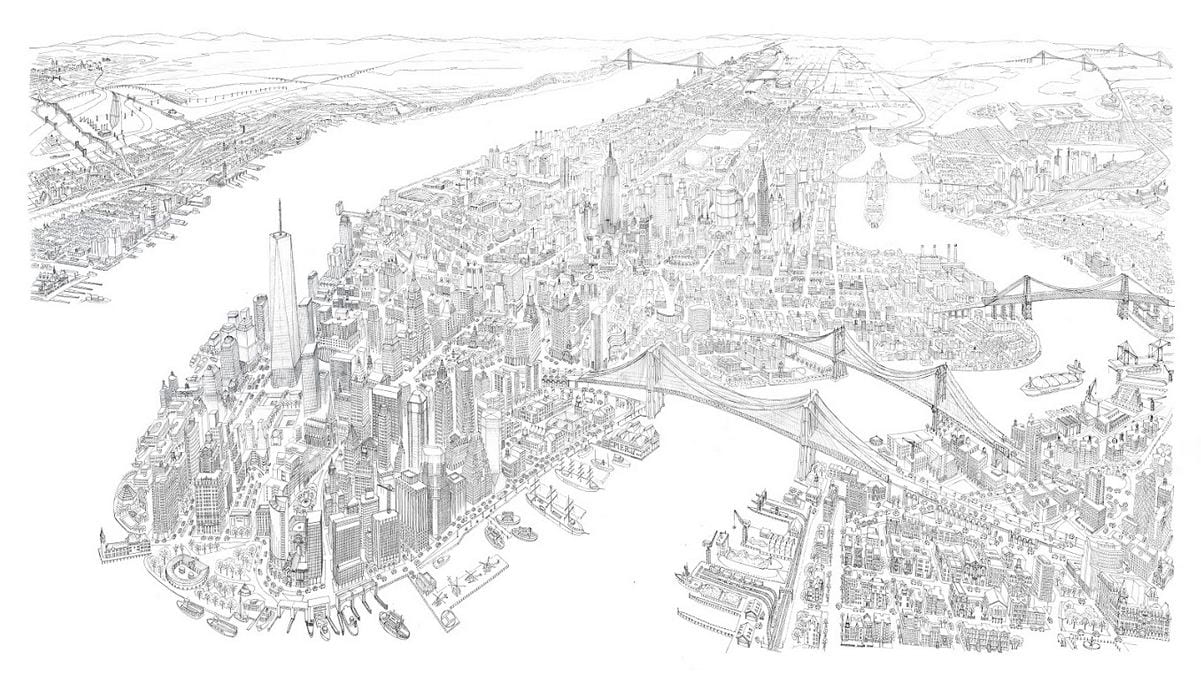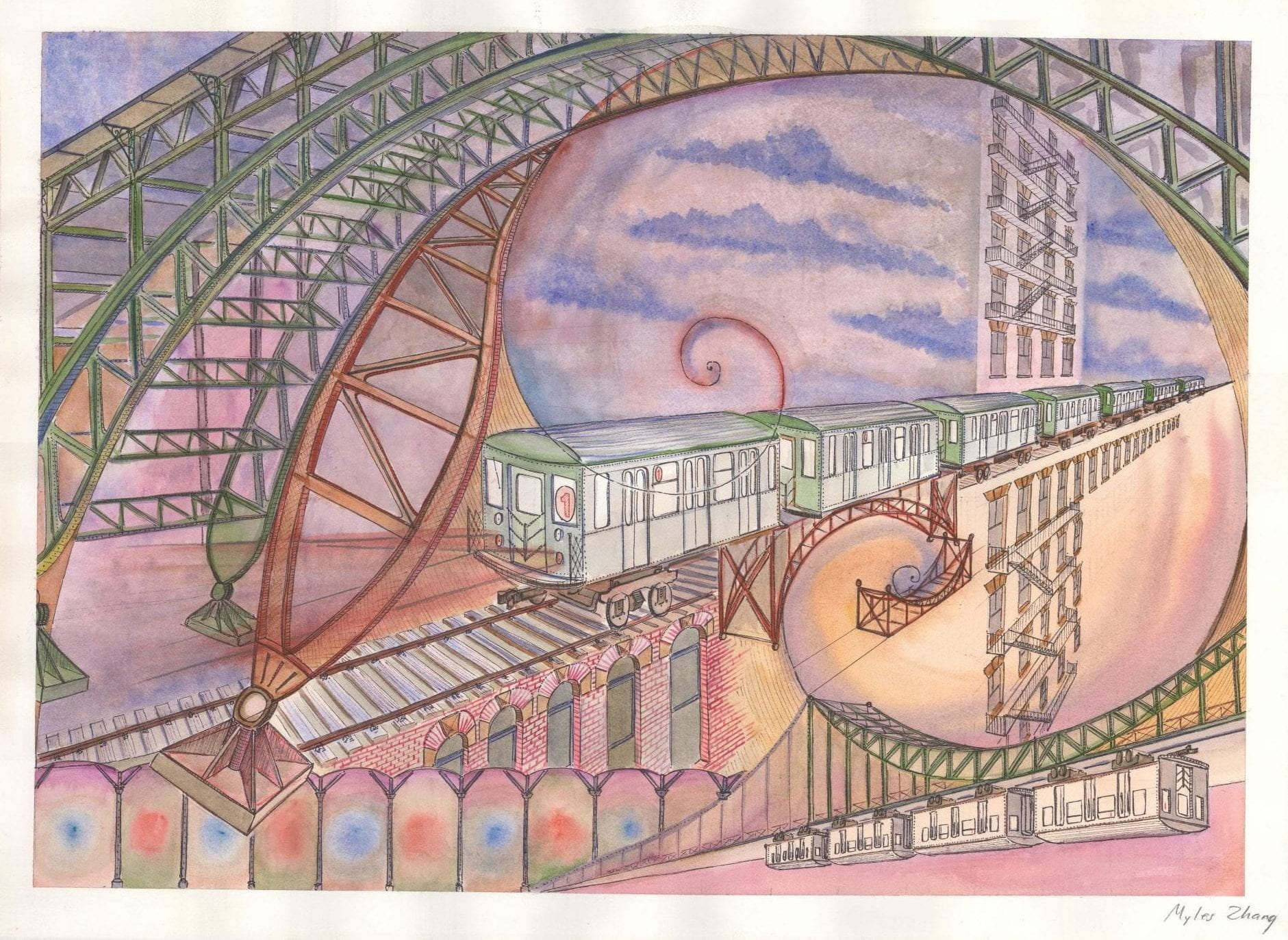
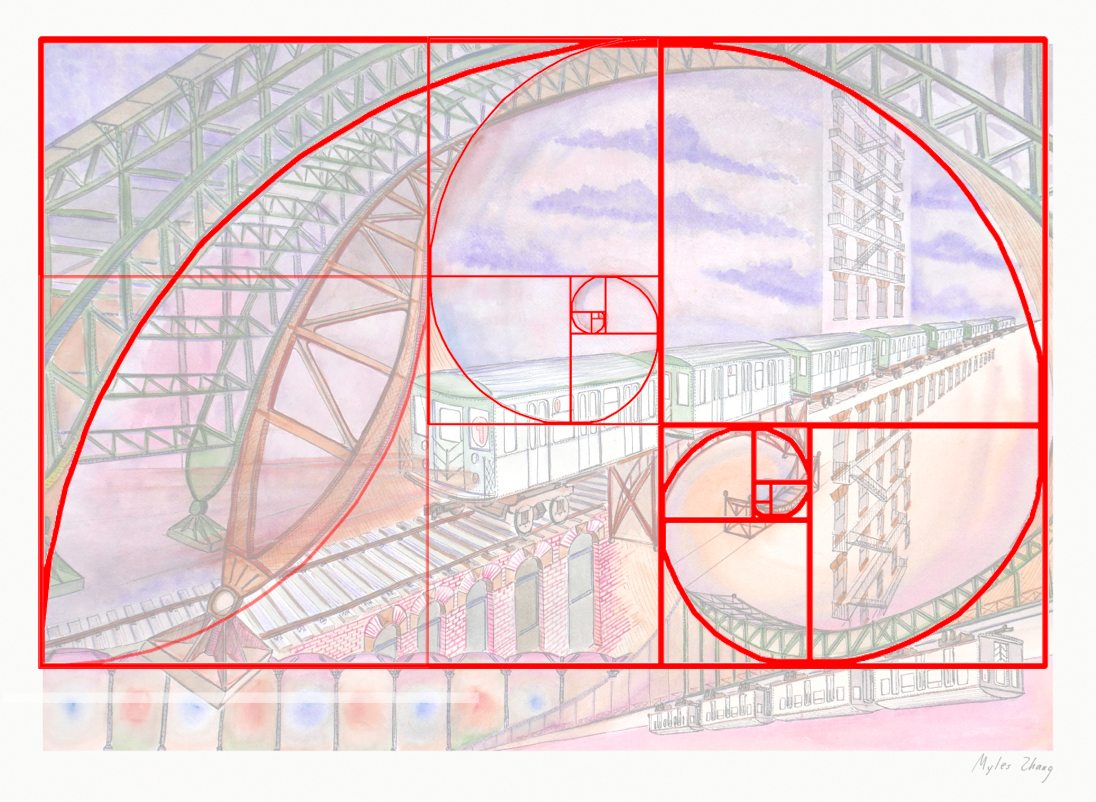
 As northbound Broadway dips down to the valley of 125th Street, the subway soars over the street. The subway viaduct is a jumble of steel slicing through the orthogonal city grid. The 125th Street viaduct is a massive arch, 250 feet from end to end, two hundred tons of mass channeled into four concrete pylons, resting on the solid bedrock of Manhattan schist. The subway is the intersection, where the underground and aboveground worlds of New York City converge.
As northbound Broadway dips down to the valley of 125th Street, the subway soars over the street. The subway viaduct is a jumble of steel slicing through the orthogonal city grid. The 125th Street viaduct is a massive arch, 250 feet from end to end, two hundred tons of mass channeled into four concrete pylons, resting on the solid bedrock of Manhattan schist. The subway is the intersection, where the underground and aboveground worlds of New York City converge.
New York City is now home to a peculiar race of people. Every day, New Yorkers step to the tune of the stoplight. Every day, they ride in sardine can subways. Like smoked ham on the butcher’s hook, they hang from subway straps. At their respective stops, they scramble on to work, home, and family. All New York is a stage, and all the men and women merely players. They have their entrances as subway doors slide open, and they time their exits to the familiar recording of “Stand Clear of the Closing Doors Please.” 1
The subway’s alphabet lines snake their way beneath the city and above the boulevards. Take the Ⓑ to Brighton Beach, the Ⓙ to Jamaica, or the Ⓕ to Forest Hills. From the towers of Midtown, to the factories of Flatbush, to the shouts of Shea Stadium, the subway is a panoply of color, motion, and people. For the price of $2.75, the world is within reach. Chinatown, Poland, Russia, Greece, India, and Italy are all neighborhoods joined by the subway’s umbilical cord. New York is a world unto herself, knit together by bands of black asphalt and steel arteries subway track.

Voice of the City by Joseph Stella, 1922.
Once wooded island of the Lenape Indians, Mannahatta,2 is now a city of immigrants and refugees: the Irish fleeing famine in 1845, the Germans fleeing Revolution in 1848, the Italians in 1871, and now waves of Czech and Chinese, Dominicans and Mexicans. As the metropolis pulsates in motion, the spirit of the city evolves with each wave of newcomers, who ride her subways, inhabit her humid tenements, and dream of home, family, and future.
In 1856, Walt Whitman published Crossing Brooklyn Ferry. He writes of immigrants and bourgeois businessmen alike, all part of “the simple, compact, well-join’d scheme, myself disintegrated, every one disintegrated yet part of the scheme.” Immigrants are the scheme of the city, the cogs of capitalism, and the human machinery of the metropolis. To each immigrant belongs her place, to each worker his seat, and to each vagabond a place in the breadline. Together they form the metropolis. Whitman also writes:
Others will enter the gates of the ferry and cross from shore to shore,
Others will watch the run of the flood-tide,
Others will see the shipping of Manhattan north and west, and the heights of Brooklyn to the south and east,
Others will see the islands large and small;
Fifty years hence, others will see them as they cross, the sun half an hour high,
A hundred years hence, or ever so many hundred years hence, others will see them,
Will enjoy the sunset, the pouring-in of the flood-tide, the falling-back to the sea of the ebb-tide. 3
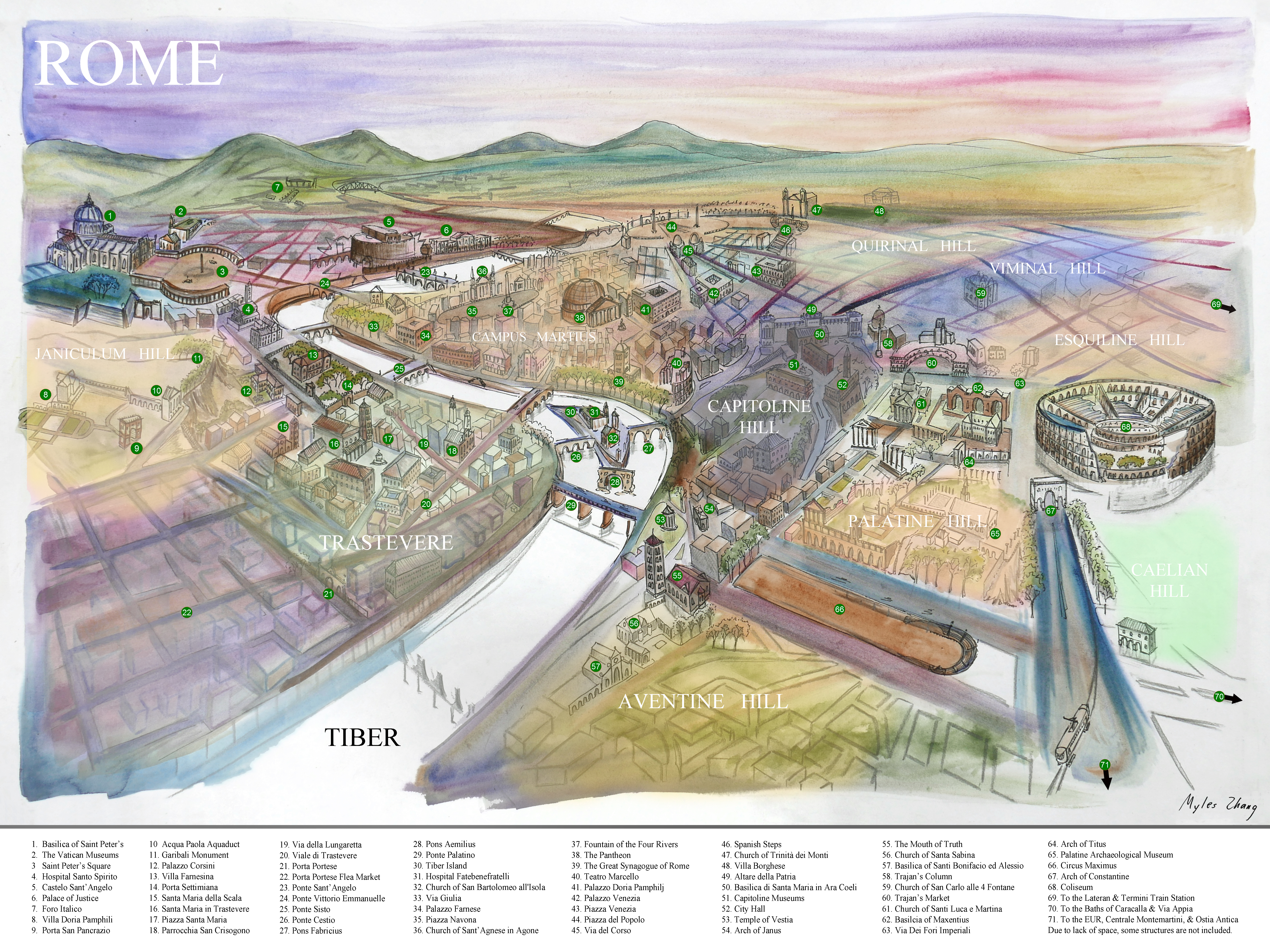
Rome is nicknamed the “Eternal City” for its ancient architecture and generations of development. New York, too, is an “Eternal City” of sorts. Its skyscrapers may rise and fall with changing tastes and a growing economy. Yet, in the face of all change to the built environment, immigrants remain the eternal constant that marks time and life in this city: a city with over three million foreign born from all corners of the world; a city whose functioning depends on the legions of immigrant window washers, janitors, and taxi drivers without whom this urban machine would screech to a halt. In 1856, Whitman wrote of a fluid and dynamic city of people in many ways like the New York of today.
.



.
New York, you, too, are home to the injustices and inequalities urban life nurtures. Hart Island, New York’s pauper’s cemetery since 1869, is the final resting place of over a million mostly unknown corpses over 150 years, the tired, the poor, and the huddled masses of immigrant New York. Over a quarter million infants are buried here, each one in an unmarked coffin made of pine, the size of a shoe box. Mass graves are three coffins deep and are buried twenty-five in a row. Nearby Riker’s Island, America’s largest jail, imprisons 10,000 a night awaiting trial in the city’s many courthouses. The South Bronx, with a per capita income $12,500, is a mere mile away from the Upper East Side, with a per capita income over $85,000. The glassy condos of Manhattan are priced at a million plus per piece, but these homes are only made possible by the immigrant workers and janitors paid $10 an hour to sweep the hallways of dust and wipe the windows of grit. Every night, these laborers, too, return to their homes in the gritty outer boroughs. They, too, ride the subway that burrows underground, as generations have before them.
In the 1880s, social reformer Jacob Riis was working on How the Other Half Lives. Through photography, he captured the squalor, darkness, and misery of New York’s impoverished immigrant community. He showed children at work in sweatshops, vagabonds at work collecting the refuse of those more fortunate. He exposed the darkness of another world a few steps from Wall Street and a few miles from the opulent mansions and department stores of Fifth Avenue and Ladies’ Mile. 4 That very same year, on March 26th 1883, the Vanderbilt Family of railroad fortune hosted the largest and most expensive costume ball in New York history, costing six million adjusted for inflation. While the idle rich came dressed as the “Count of Monte Cristo” and “Otho the Barbarian,” the poor slept in squalor a carriage ride away in the Lower East Side. As the New York Sun reported three days later, “[This] festivity represents nothing but the accumulation of immense masses of money by the few out of the labor of the many.” 5
.
- 1890 cover page of Jacob Riis’ book
- Garment sweatshop with child labor (Jacob Riis photographer)
- Lower East Side
- The Vanderbilt Mansion
- With a taxidermied cat on her head, Miss Strong attends the Vanderbilt costume ball.
.
Though a century has passed since Riis, New York still is a city of social contrasts and economic disparities. Ironically, Jacob Riis’ Lower East Side is now a fashionable community for the upper middle class. All the same, the eternal New York City of immigrants endures in the outer boroughs of Flushing, Queens, Jackson Heights, South Bronx, and Bedfort Stuyvesant. In many regards, their social condition is not too different from Riis’ era. His images of New York testify both to how much and to how little New York has changed. America’s Eternal City still is a place of great injustices, but it is also the place where many of these injustices were first confronted and solved by the city’s activists and artists.

Subway by George Tooker, 1950.
As E.B. White wrote in 1949: “The city is like poetry: it compresses all life, all races and breeds, into a small island and adds music and the accompaniment of internal engines. The island of Manhattan is without any doubt the greatest human concentrate on earth, the poem whose magic is comprehensible to millions of permanent residents but whose full meaning will always remain illusive.” 6 Over 400 years since New York’s founding in 1609 by the Dutch, these words remain true as each generation of Men and Women creates the City in their own image. 7
New York, you have not the tree-lined boulevards of Paris, the tradition and pomp of London, or the antiquity of Rome. However, in your diversity of people, cuisine, and culture, you are something far greater. You are home to a city of strangers, a city of neighborhoods, a city of sound, a city of subways, taxis, and buses flowing from the canyons of Midtown to the quiet bedrooms of Westchester and Park Slope, like rivulets of water. Flow on city, flow with the tide, and glide through the eras. Flow on Isle of Mannahatta for “a hundred years hence,” like a ship anchored on bedrock between two proud rivers.
https://mcnyblog.files.wordpress.com/2013/08/sun-mar-29-1883-critical.pdf
Endnotes
- Adapted from “All the World’s a Stage” by William Shakespeare ↩
- Before Manhattan was settled by Dutch explorers in 1609, it was known by the local Lenape Indians as Mannahatta. ↩
- “Crossing Brooklyn Ferry” from Leaves of Grass by Walt Whitman, 1856. ↩
- How the Other Half Lives by Jacob Riis, 1890. ↩
- The New York Sun, March 29, 1883. ↩
- Quoted from Here is New York by E.B. White in 1949. ↩
- “So God created mankind in his own image.” Genesis 1:27. ↩









































































































































































































































 .
.