Ironically, the most unequal and dystopian of societies are often founded on utopian principles. Utopias, almost by their very nature, have undertones of conformism and oppression. From Plato’s Republic of strict castes and rampant censorship to Thomas More’s Utopia of puritanical laws and slavery, a utopia for the few is often a dystopia for the many. The question then arises: How do the benefactors of utopia confront its detractors? Utopia has several choices. It can maintain its monopoly on media and education, strangling nascent free thought before it grows into free action. Or it can physically punish and oppress free thought, which requires systems to detect and punish dissent. Detection requires gathering information about the populace. Punishment requires control and physical torture: the police, the army, and the prison. Ironically, to maintain power against its critics, utopia often adopts trappings of dystopia.[1]
Despite the seeming differences between them, many utopias and dystopias often resemble the panopticon, a model of the ideal surveillance state. In fact, panopticon, dystopic police state, and utopian society share common goals: total observation, total power, and unquestioned control.
.
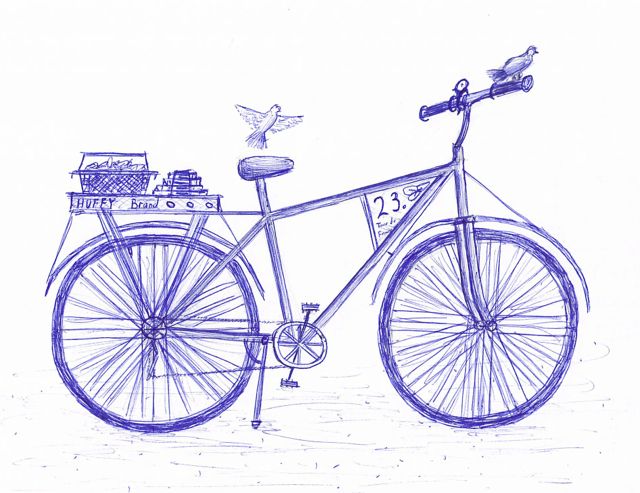
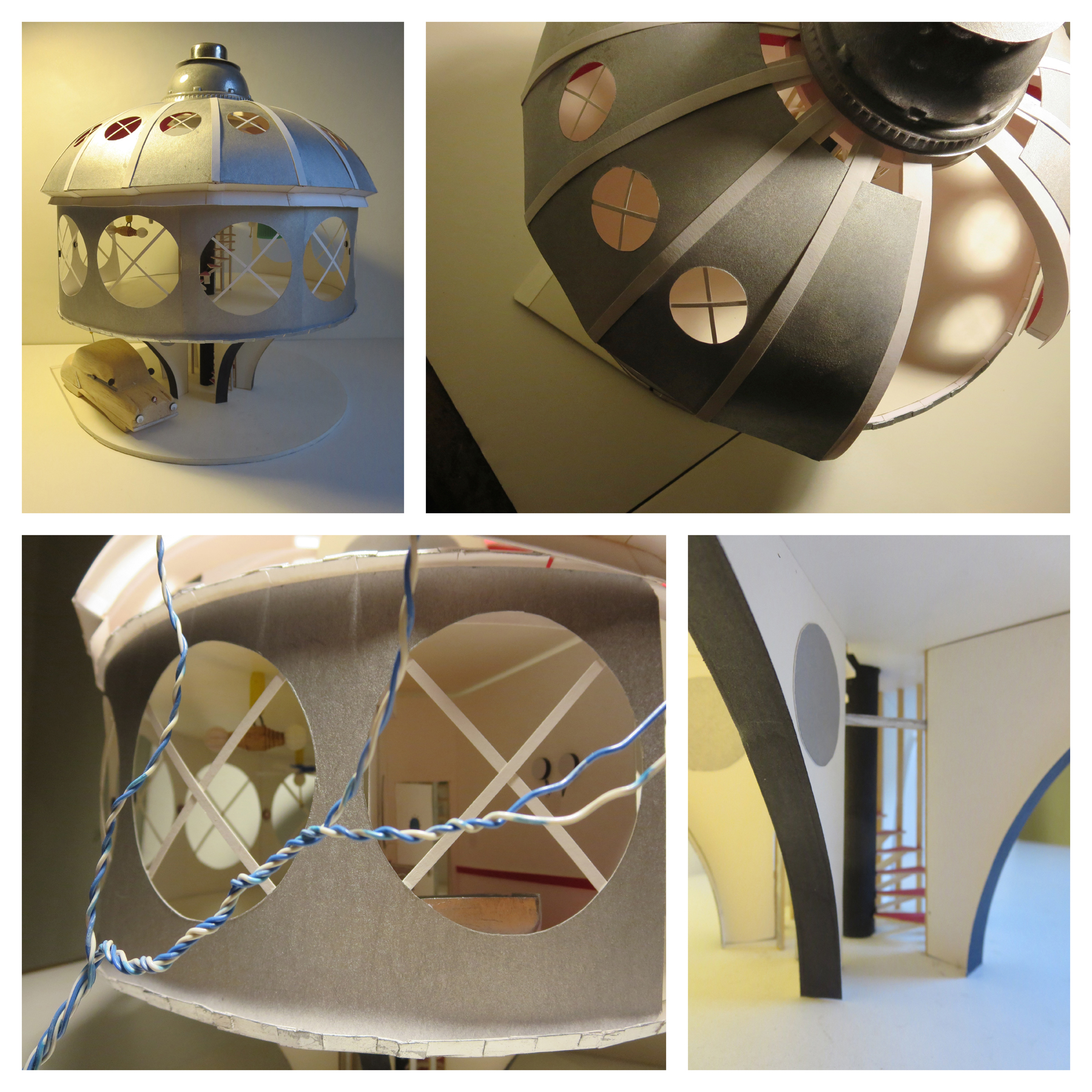
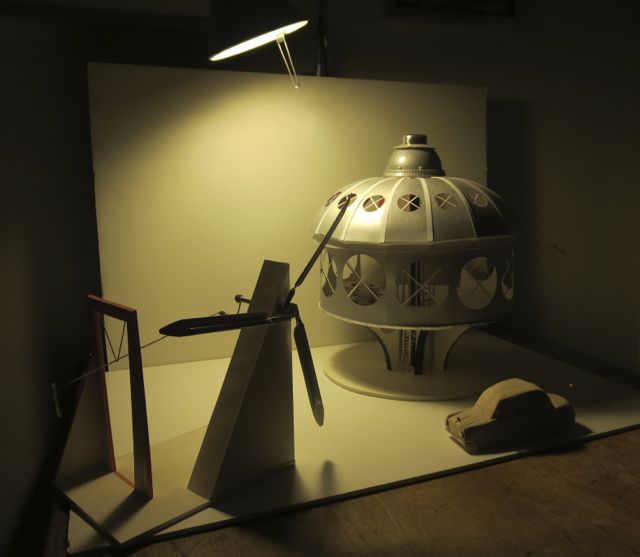
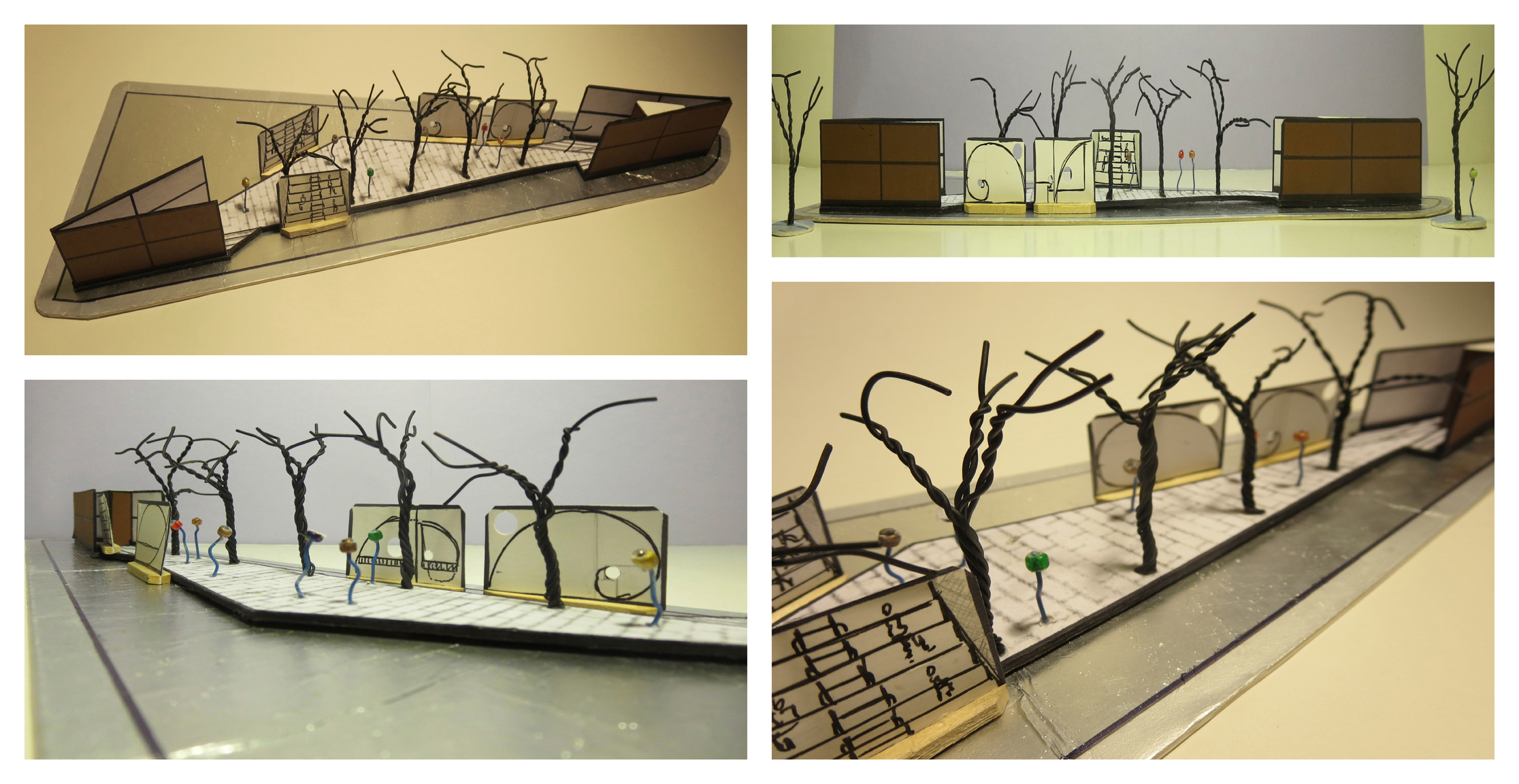
The panopticon models the workings of a society.
The panopticon was initially an architectural concept for the ideal prison. Conceived in 1791 by Jeremy Bentham, an English-born philosopher, social reformer, and utopian thinker,[2] the panopticon embodies the ideals of observation, control, and discipline. In its physical form, the panopticon is a circular prison with cells ringed around a central tower from which prisoners can be watched at all times. This slender central tower contains a covered guardroom from which one guard simultaneously surveys hundreds of prisoners (see image below). The panopticon aims for constant surveillance and prisoner discomfort. In this all-seeing system, dissent is detected and discipline is enforced.
Read More
.