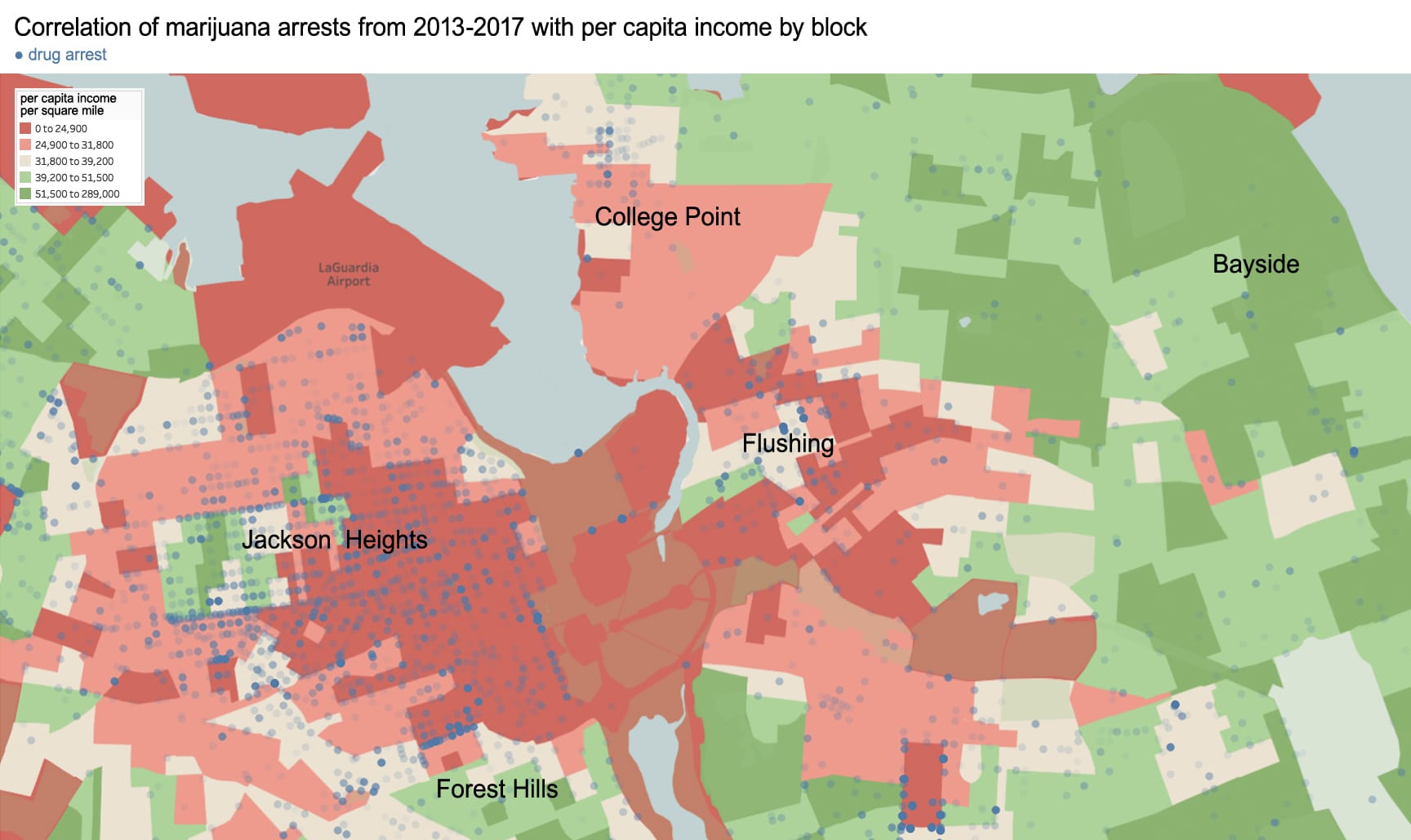
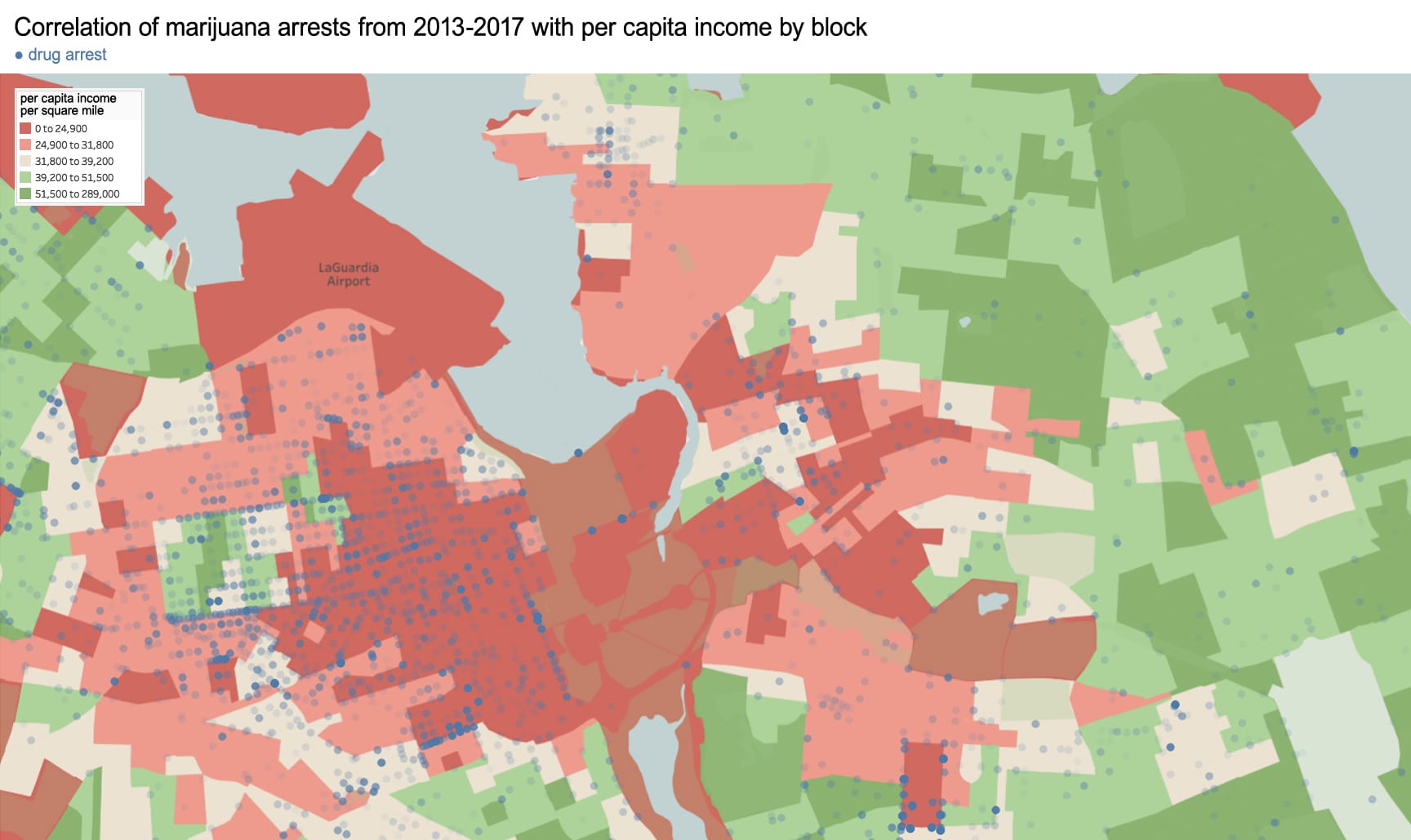
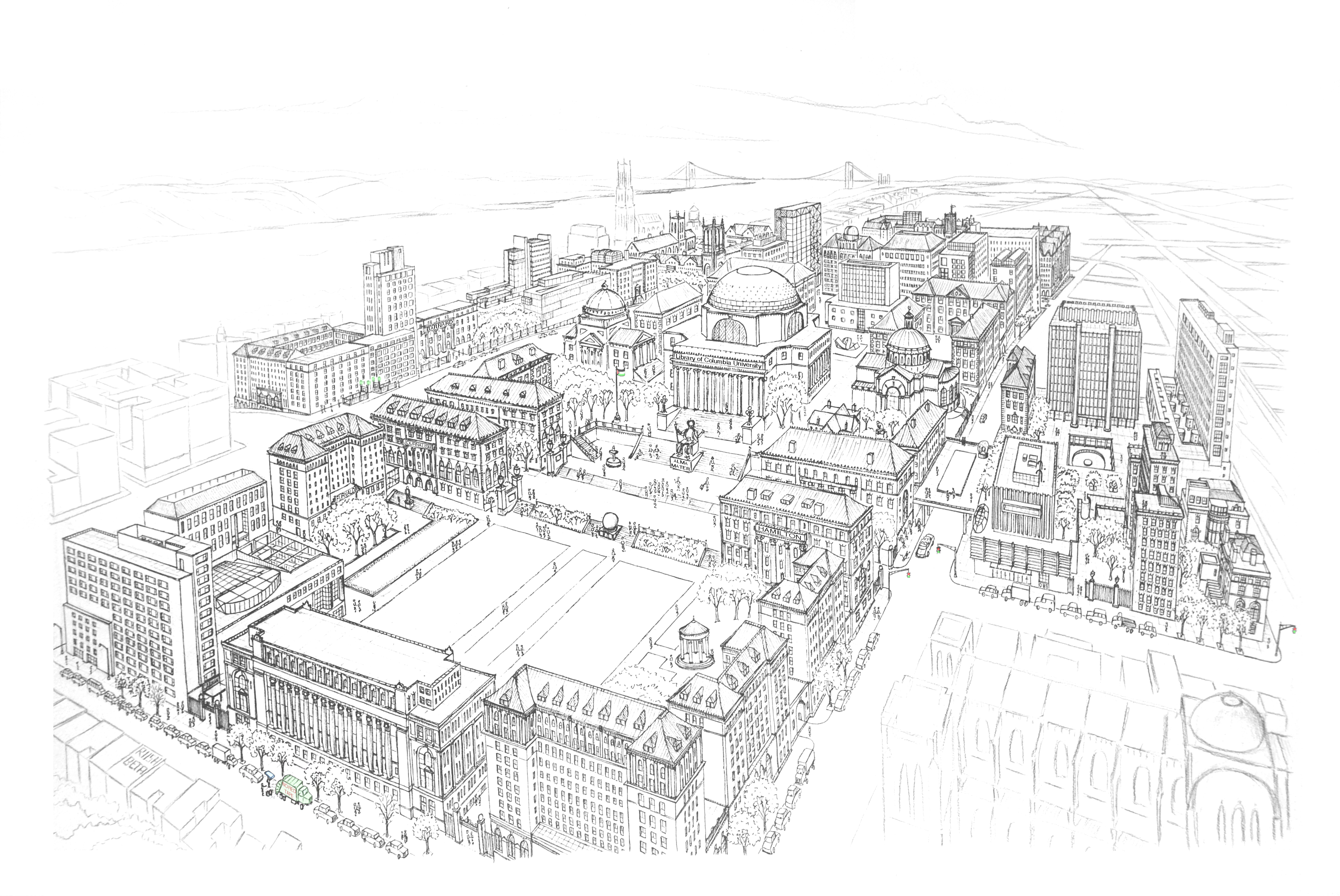
Originally published in the 2018-19 edition of the Asia Pacific Affairs Council journal with help from Seeun Yim at Columbia University’s Weatherhead East Asian Institute, pages 18-20
.

Canal and Mott Street
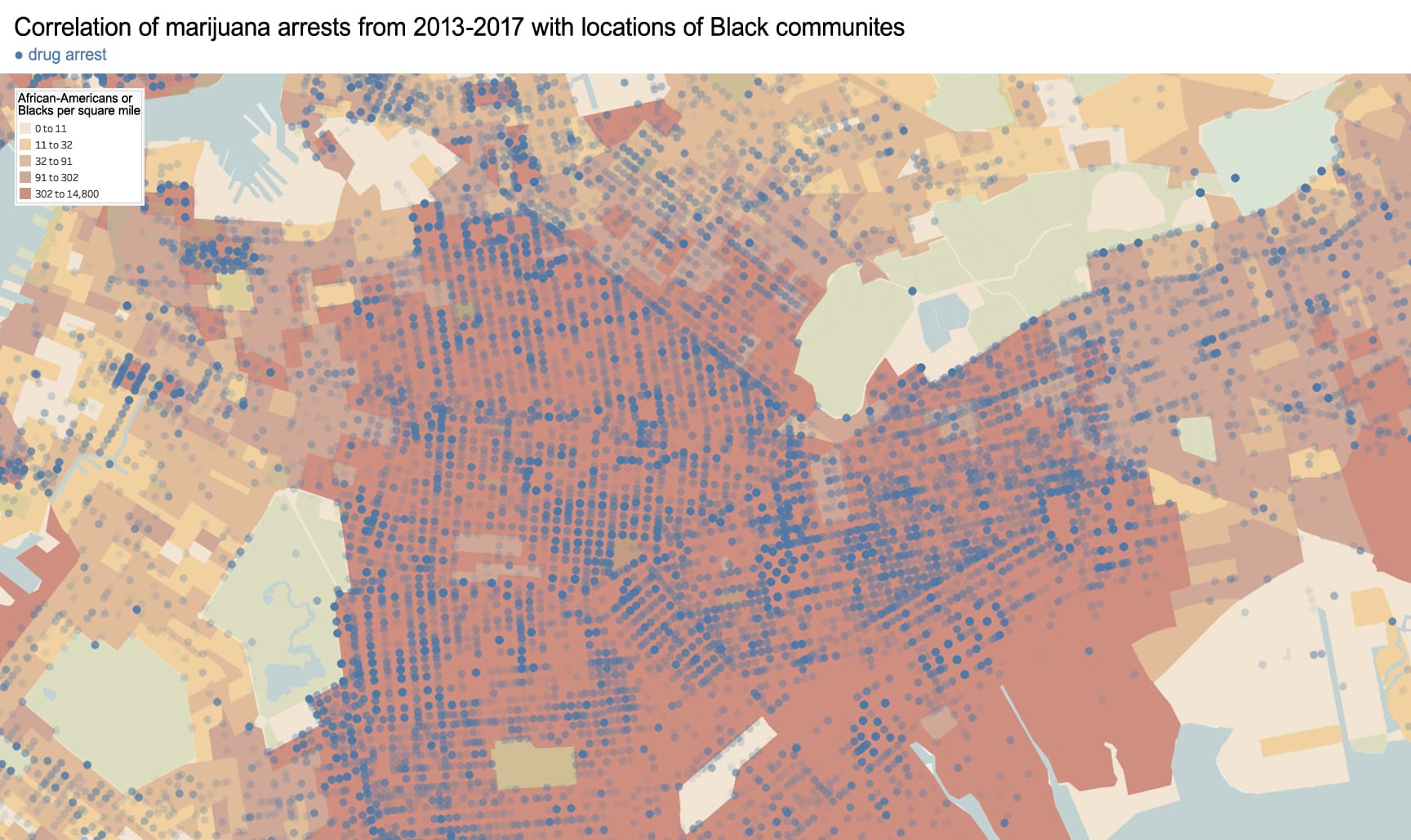
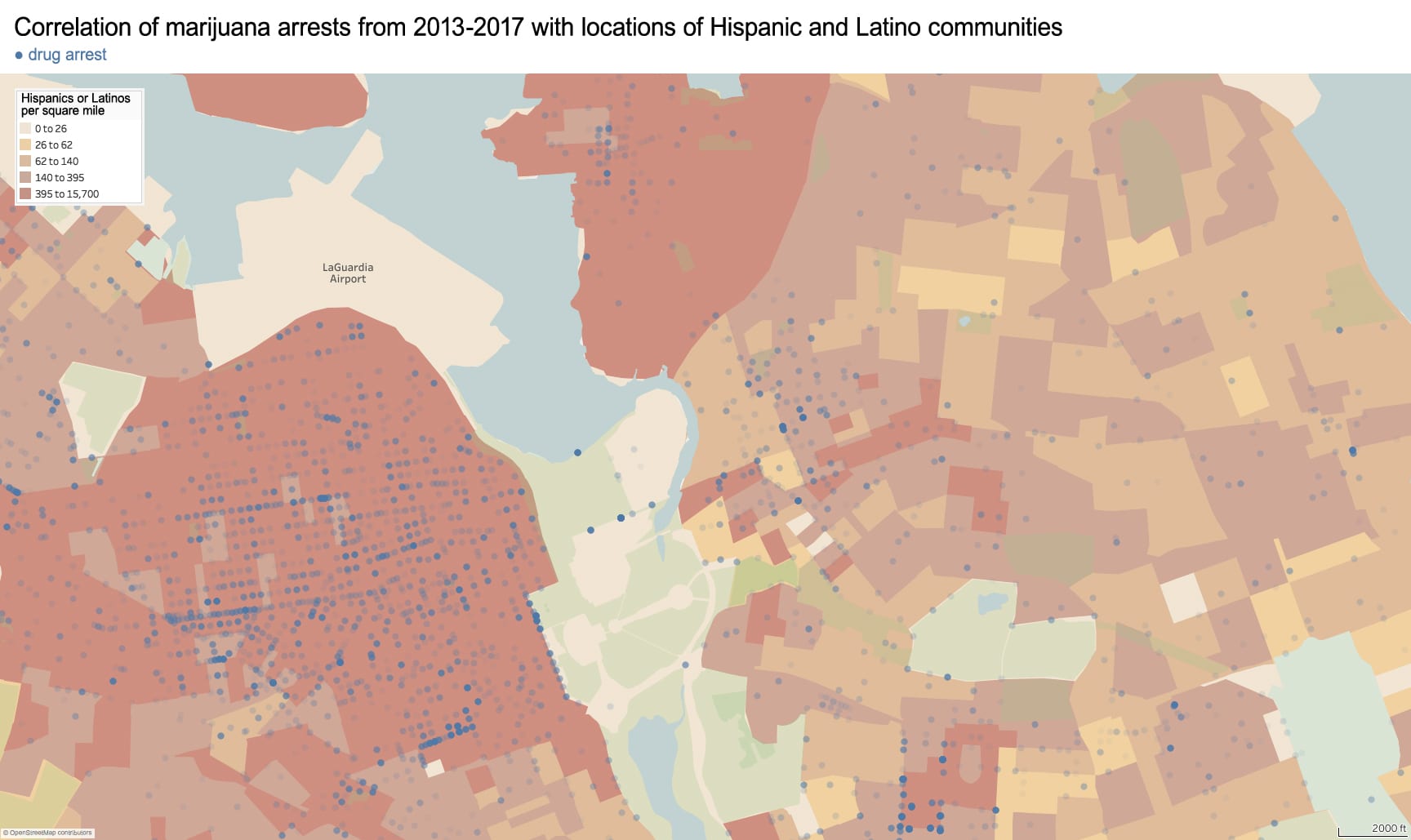
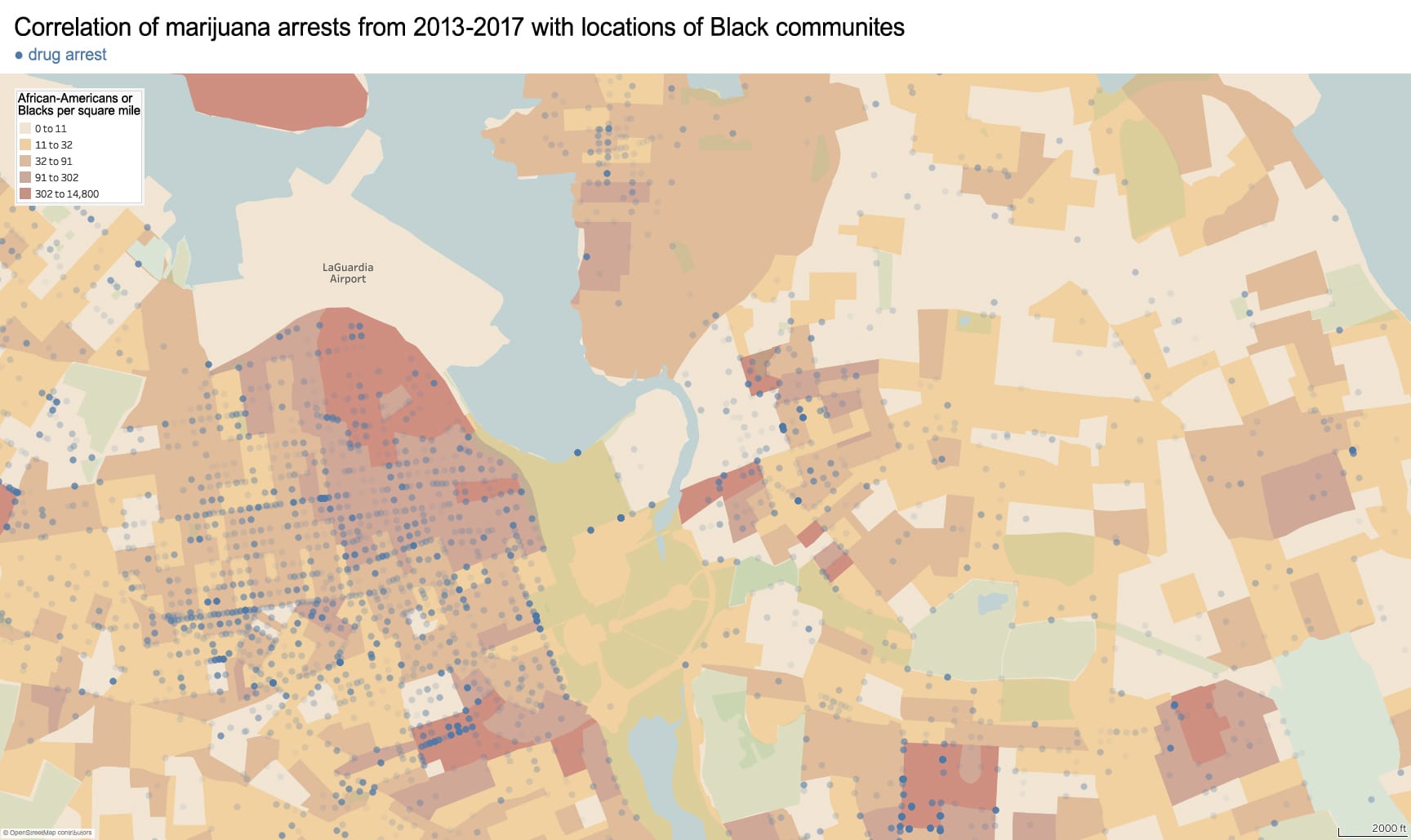
In 1882, the Chinese Exclusion Act restricted Chinese immigration to the US, prohibited Chinese females from immigrating on grounds of “prostitution,” and revoked the citizenship of any US citizen who married a Chinese male. The consequences of this xenophobic legislation motivated Chinese immigrants to flee racial violence in the American West and to settle in Manhattan’s Chinatown. With a population now of around fifty thousand (2010 census), this remains the largest ethnically Chinese enclave in the Western Hemisphere.

Barbershop Row on Doyers Street
Thanks to New York’s geographic location as a port city with high industrial employment and easy connections to the American interior, this city became the primary point of entry for waves of immigrant groups in the nineteenth century: Irish, Germans, Italians, and Eastern Europeans. What makes the Chinese different, though, is the survival and resilience of the immigrant community they created. Other immigrant groups – namely the Germans and Irish – converged around large neighborhoods and surrounded themselves with familiar languages and businesses. Of these enclaves, all have since disappeared. The children of these first-generation immigrants successfully assimilated into American society, earned higher incomes than their parents, and therefore chose to disperse to non-immigrant neighborhoods with better housing stock and schools. Yet, the Chinese remained.
The resilience of this community results from a confluence of factors: cultural, geographic, and political. Of innumerable immigrant groups to the US, the Chinese were among the only to have the most restrictive laws placed on their immigration. This stigma drove them toward three types of low-paid labor – with which white Americans still deeply associate with the Chinese – laundries, restaurants, and garment manufacturing. Like the Chinese, other groups – particularly Irish-immigrant females – began working in these professions, but they soon climbed the social ladder.

Mosco Street and Mulberry Bend
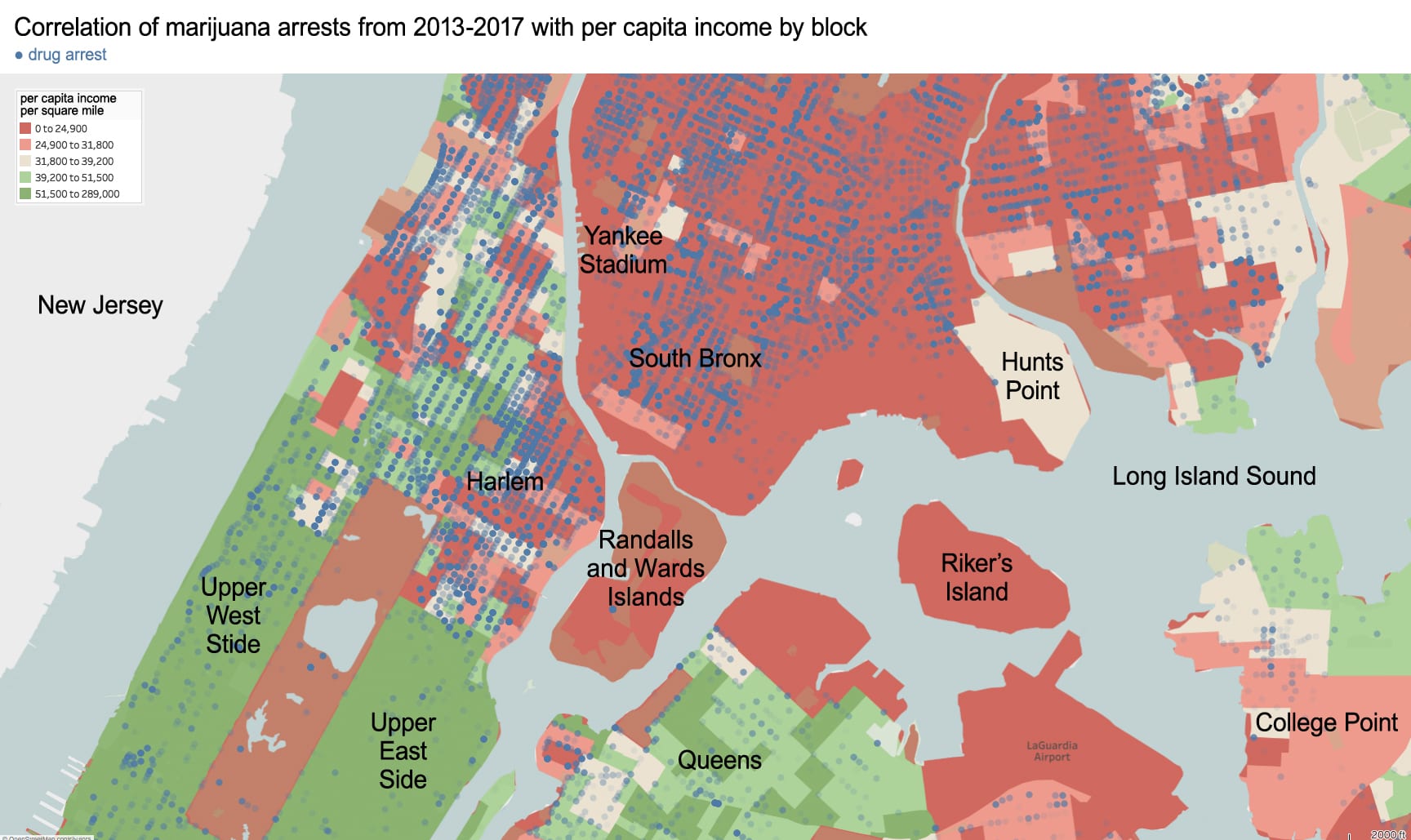
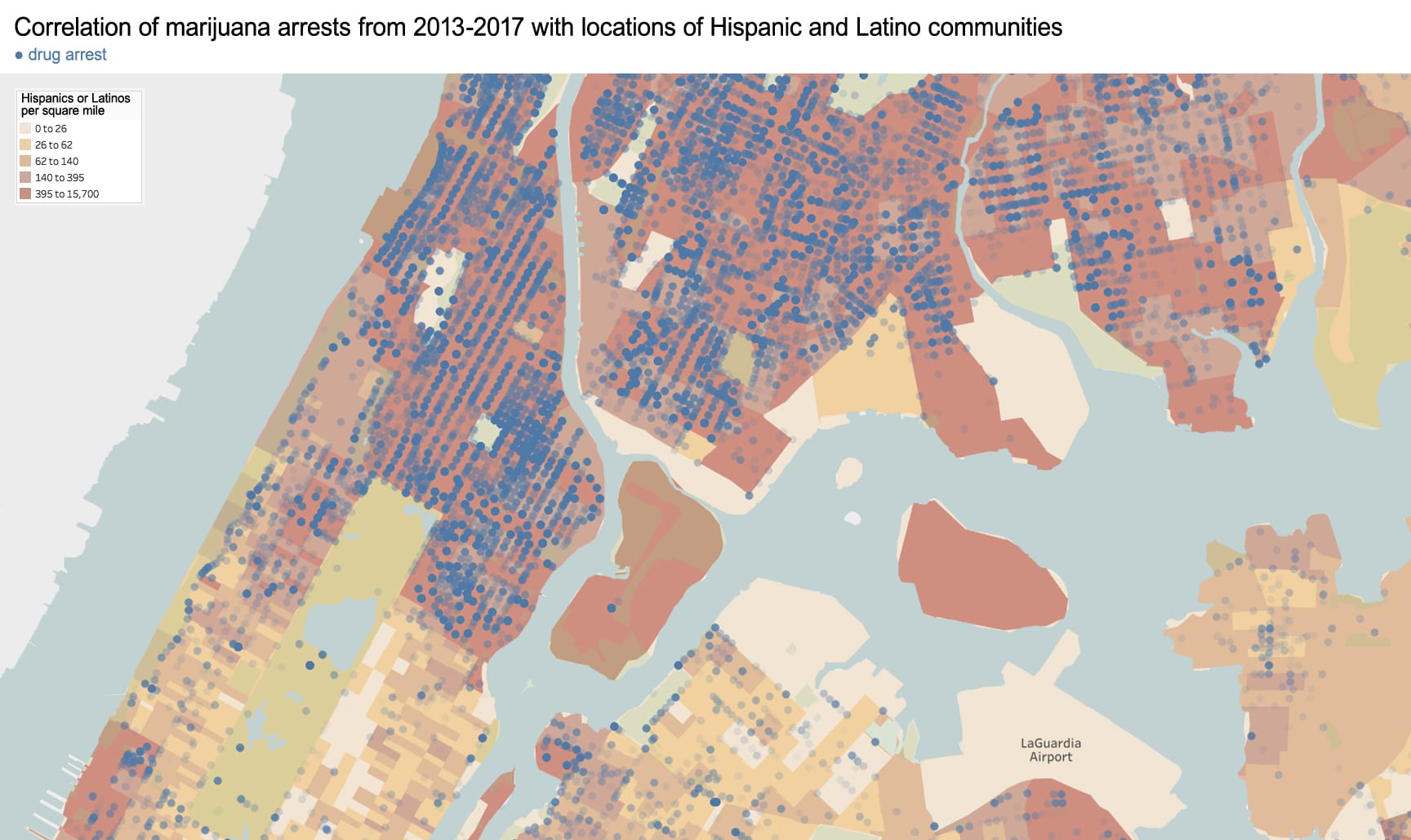
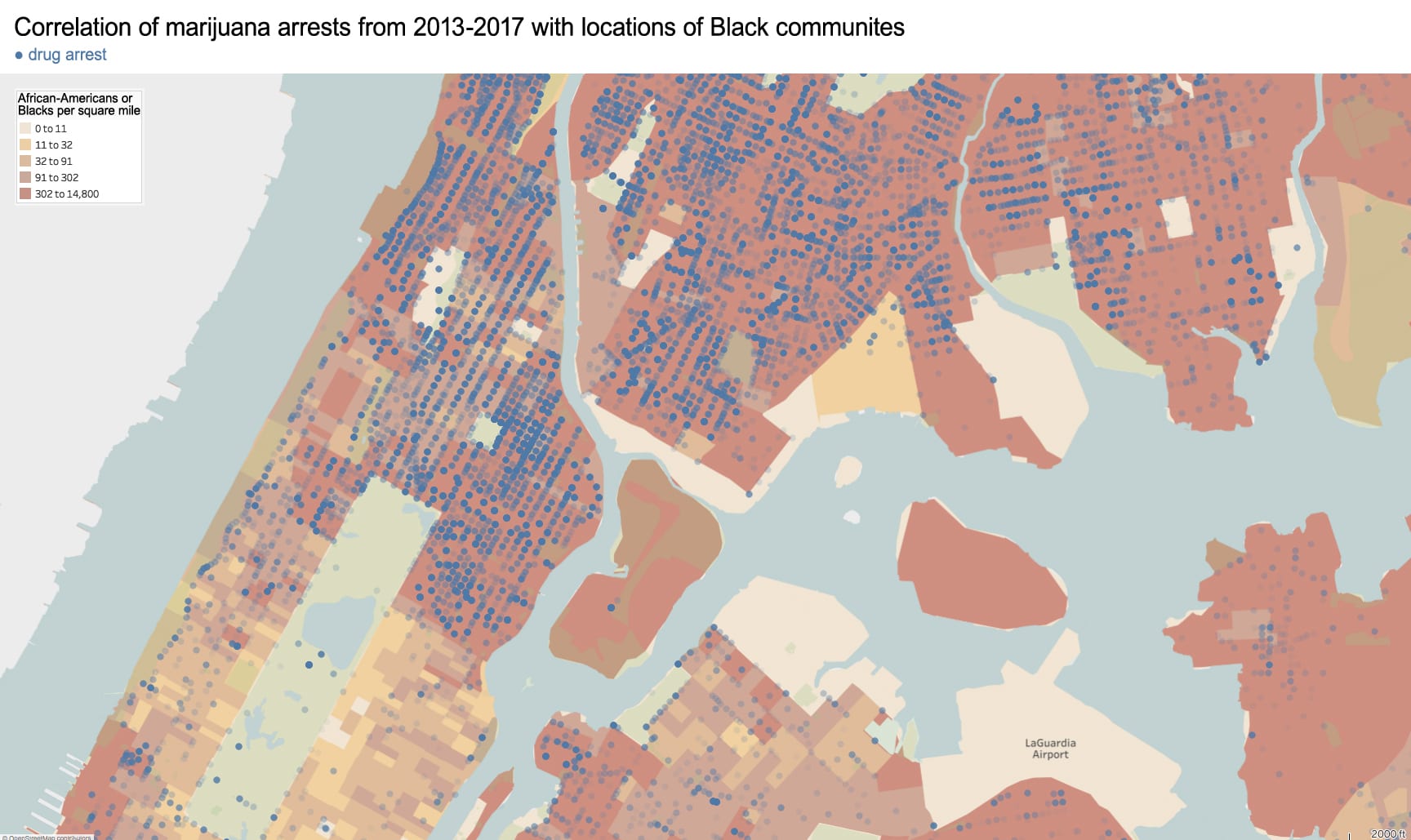
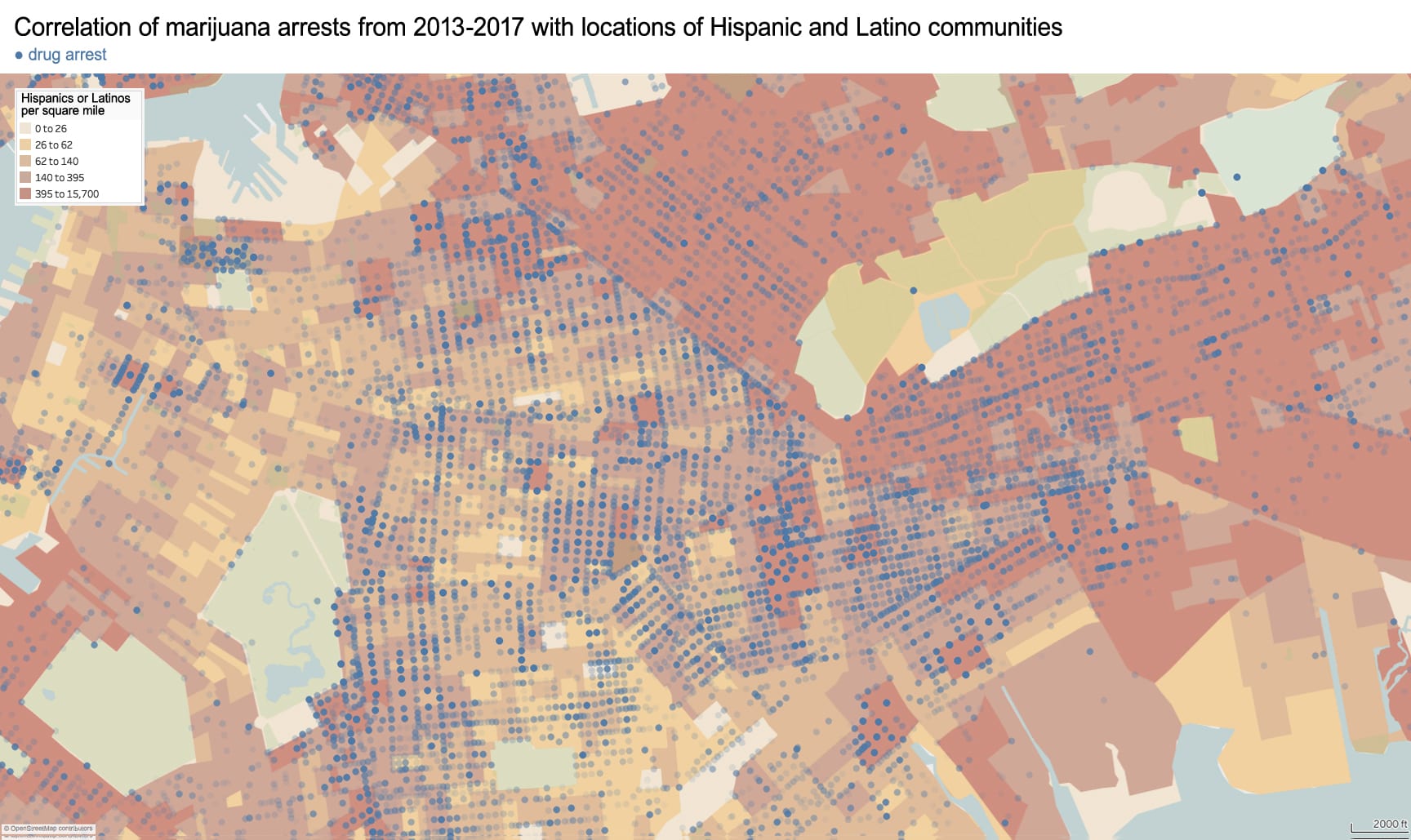
As an architectural historian, I see that the political and racial agenda of exclusion is imprinted in the built environment of Chinatown. To present this neighborhood’s geography: For most of its history, Chinatown was bordered to the north by Canal Street, to the east by Bowery, and to the South and West by the city’s federal courthouse and jail. The center of this community lies on the low wetland above a filled-in and polluted lake called the Collect Pond. Historically, this area contained the city’s worst housing stock, was home to the city’s first tenement building (65 Mott Street), and was the epicenter for waterborne cholera during the epidemics of 1832 (~3,000 deaths) and again in 1866 (1,137 deaths). The city’s first slum clearance project was also in Chinatown to create what is now present-day Columbus Park.
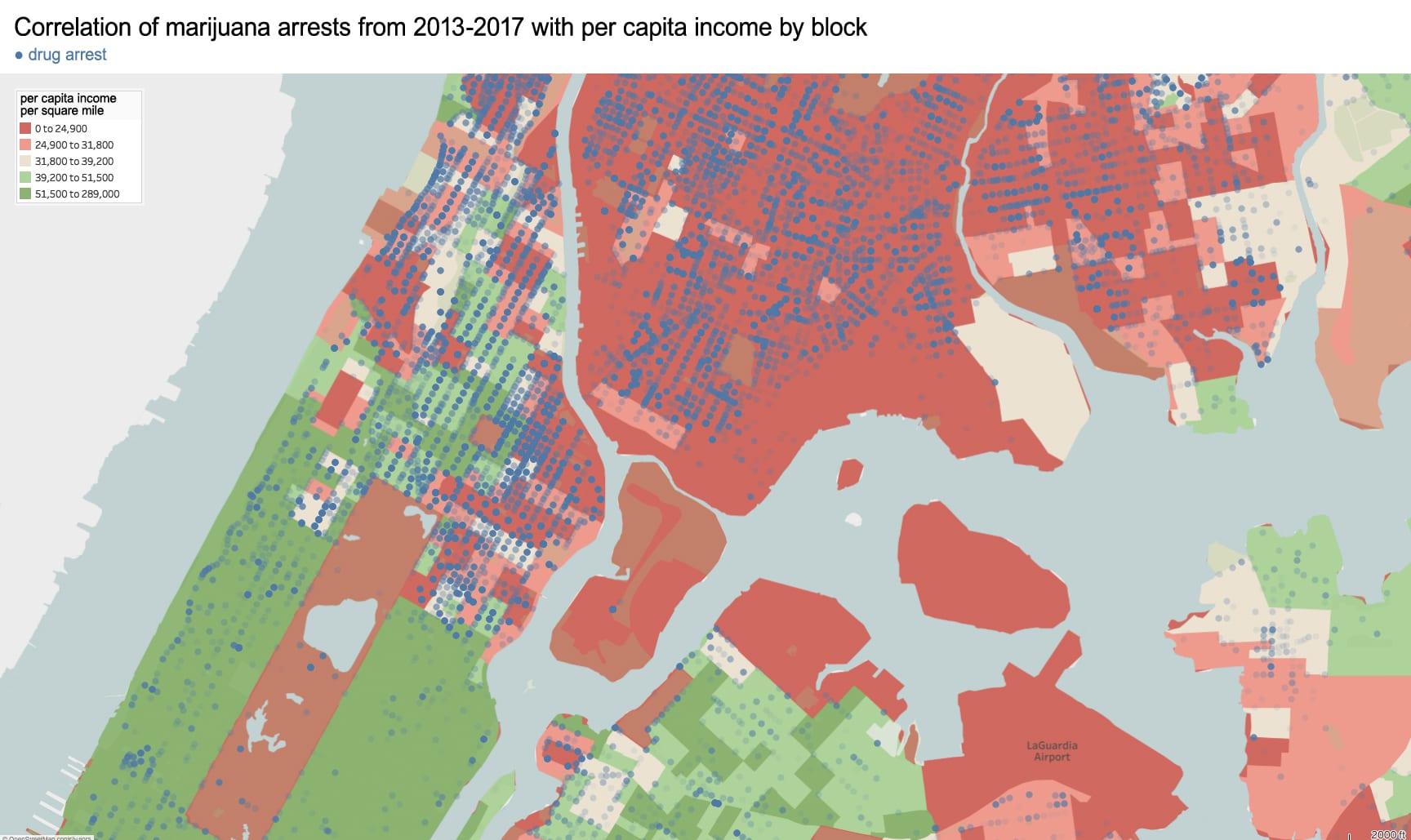
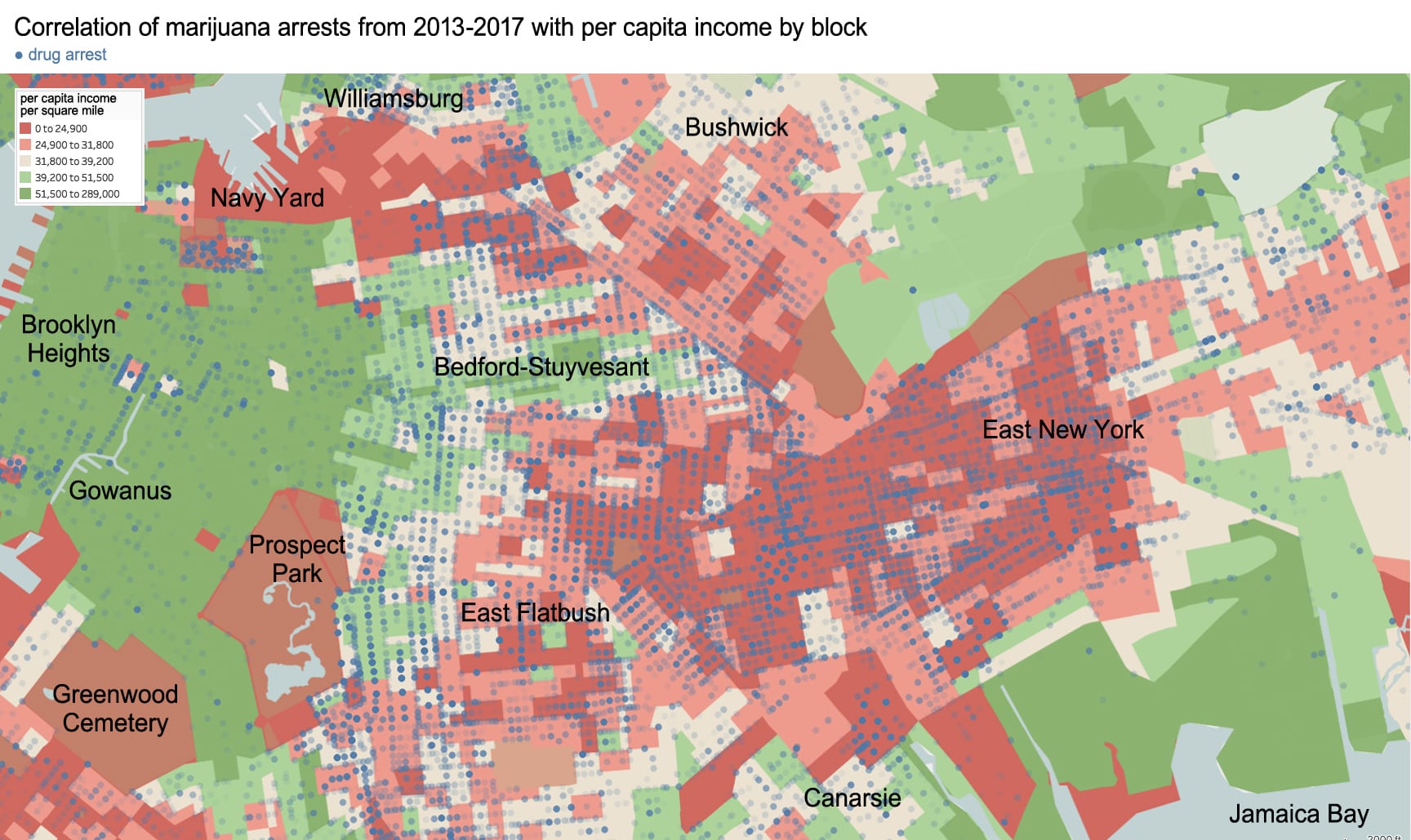
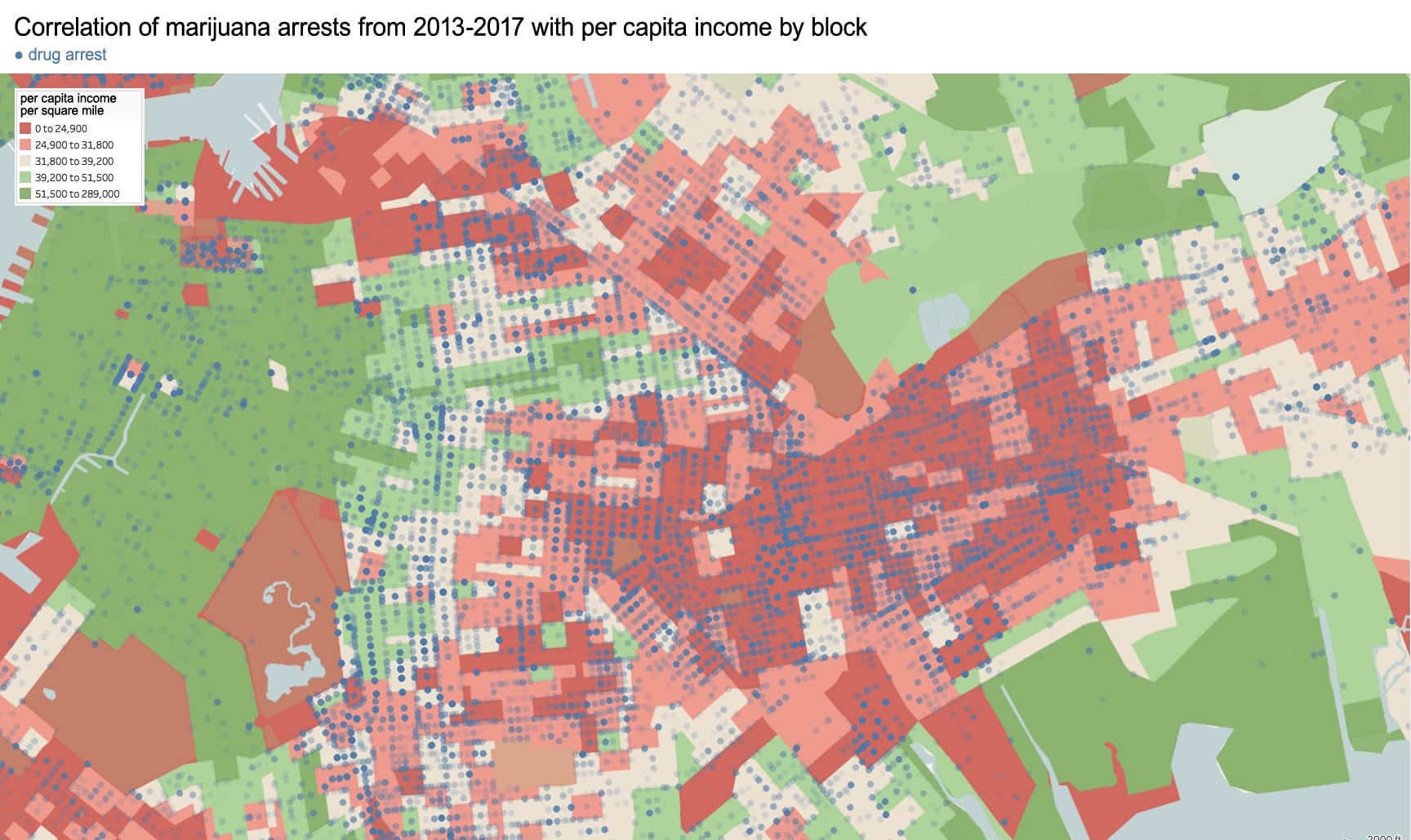
Race-based policies of exclusion can take different forms in the built-environment. The quality of street cleaning and the frequency of street closures are a place to start. Some of the city’s dirtiest sidewalks and streets are consistently located within Chinatown – as well as some of the most crowded with street vendors, particularly Mulberry and Mott Street). Yet, as these streets continue northward above Canal Street, their character changes. The street sections immediately north in the enclave of Little Italy are frequently cleaned and closed for traffic most of the year to create a car-free pedestrian mall bordered by upscale Italian restaurants for tourists. The sections of Mulberry Street in Chinatown are always open to traffic and truck deliveries.

Grocery Store at Bayard and Mulberry Streets
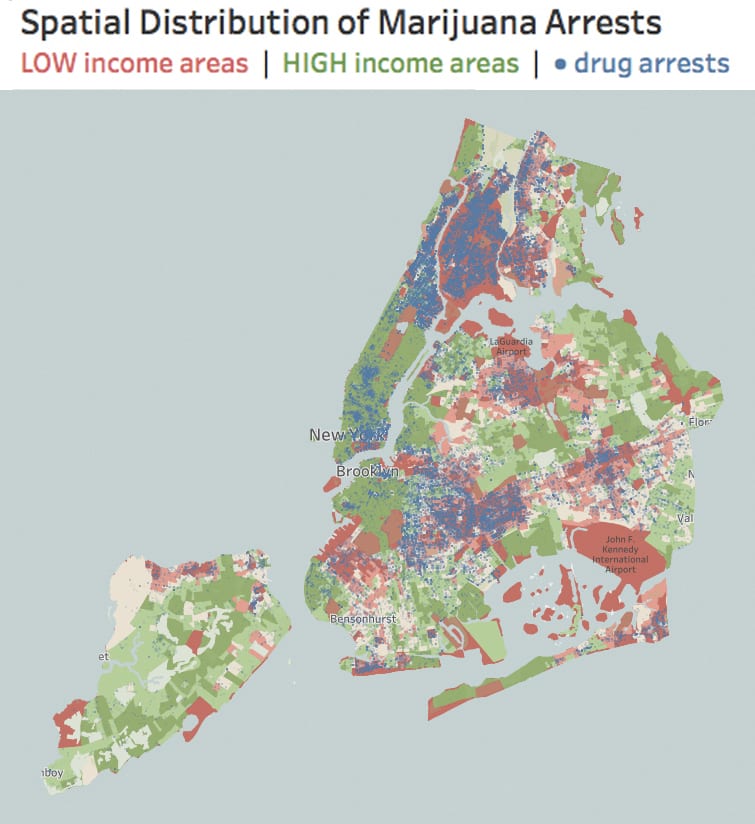
Unequal treatment continues when examining the proximity of Chinatown to centers of political power and criminal justice. Since 1838, the city’s central prison (named the Tombs because of its foreboding appearance and damp interior) was located just adjacent to Chinatown. The Fifth Police Precinct is also located at the center of this community at 19 Elizabeth Street. Although Chinatown was ranked 58th safest out of the city’s 69 patrol areas and has a crime rate well below the city average, the incarceration rate of 449 inmates per 100,000 people is slightly higher than the city average of 443 per 100,000. This incarceration rate is also significantly higher than adjacent neighborhoods like SoHo that have a rate well below 100 per 100,000. NYC Open Data reveals this neighborhood to be targeted for certain – perhaps race-specific and generally non-violent crimes – like gambling and forgery. Over half of all NYPD arrests related to gambling are in Manhattan Chinatown. Similarly, the only financial institution to face criminal charges after the 2008 financial crisis was Chinatown’s family-owned Abacus Federal Savings Bank – on allegations of mortgage fraud later found false in court by a 12-0 jury decision in favor of Abacus. Abacus provided mortgages and unconventional financial services to the kinds of immigrants traditionally locked out of the banking system, and therefore denied the means to climb the social ladder. The mistreatment of the Chinese in America both past and present is part of a larger anti-China agenda.
When it comes to tourism, Americans seem to have a paradoxical relationship with Chinatown’s “oriental” culture and cuisine. On the one hand, there is a proclaimed love of East Asian cuisine and art, as evidenced by the profusion of Asian-themed restaurants for tourists, or as evidenced by the phenomenon in art history for western artists (and particularly French Impressionists) to incorporate decorative motifs from East Asian woodcuts and ceramics into their work. On the other hand, there is simultaneously exclusion of the people who created this Chinese food and art from political power and social mobility. Still today, Americans seem to want competitively priced Chinese products without suffering the presence of the foreigners who produced these products.

Forsyth and Delancey Street
Let us clarify one thing: The division in Chinatown is not “apartheid” in the strict sense. It is perhaps a division more subtle and difficult to notice. It expresses the kind of unequal treatment – antiquated housing, crowded conditions, and municipal apathy – that face many immigrant groups in America. The built environment of Chinatown is something altogether more complicated and layered with other ethnic groups, too. For instance, the Church of the Transfiguration in the center of Chinatown now has a majority Asian congregation, even though it was founded in 1815 as a German and Lutheran church. Similarly, some of the funeral parlors on Mulberry Bend have Italian origins and old Italian men in the funeral bands. This neighborhood is also in the active process of gentrification with rising rents pushing out older Asian businesses.
If and when the Chinese become fully integrated into American society, how should the architectural fabric of this immigrant enclave be preserved, considering that its very existence is a marker of race-based exclusion and the century-long challenge of the Chinese in America?
.
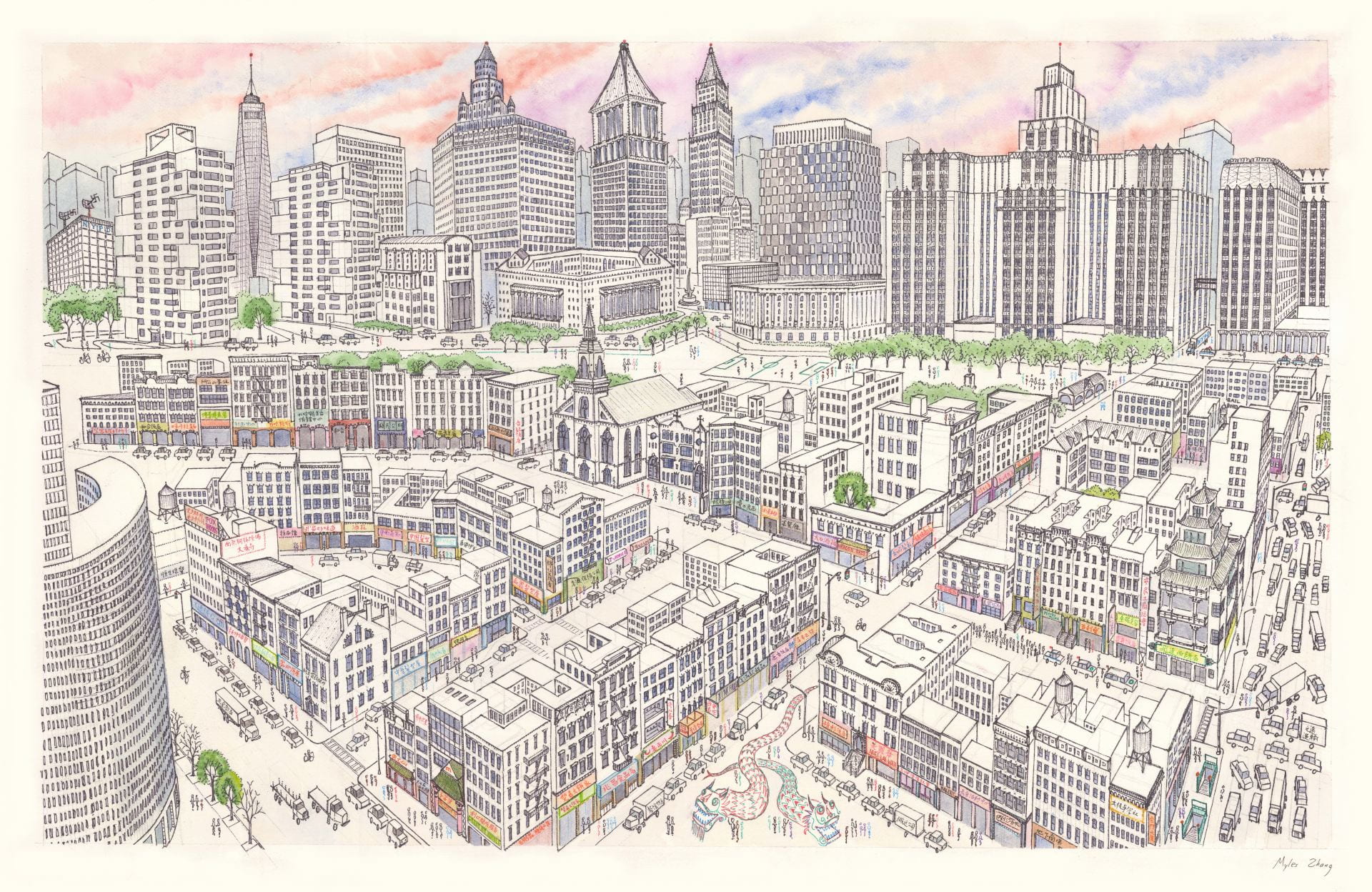

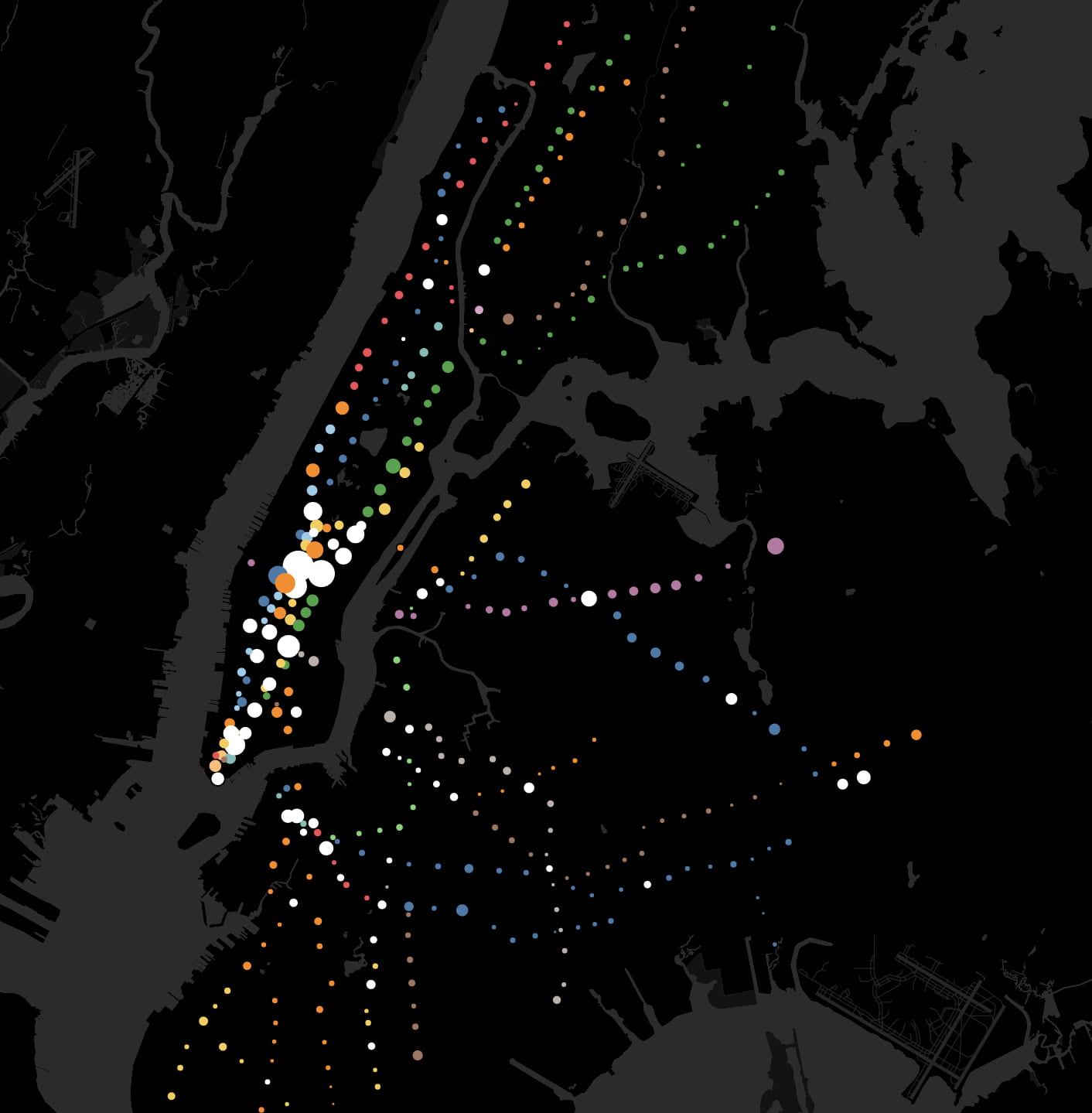
This time-lapse of Manhattan Chinatown took sixty hours to complete and measures 26 by 40 inches. Chinatown’s tenements are in the foreground, while the skyscraper canyons of Lower Manhattan rise on top. This shows the area of Chinatown bordered by Bowery, Canal Street, and Columbus Park.
.
Chinese music: Feng Yang (The Flower Drum)