According to the Metropolitan Museum of Art
.
Related: Data analysis and visualization of 120,000 works in the Museum of Modern Art
.
.
In this film, each colored dot indicates one location represented by art in the Met’s online database. Dot location indicates artwork provenance. Dot size indicates the number of objects from this place. The time each dot appears corresponds to the year this work was created. This data is assumed to be an accurate sample size.
.
Over the past few years, the Metropolitan Museum has catalogued over 25% of its holdings online. This represents ~590,000 objects, covering over 5,000 years of human history from 17 curatorial departments. The diversity of objects in a museum’s collection (and the amount of contextual information known about these objects) may reflect the kinds of narratives a museum can curate about artistic and global history. This visualization charts the provenance and year of production of every single object that is catalogued on the Metropolitan Museum website, whenever this information is known.
The geography of art history is uneven. Certain regions, particularly cities, are home to diverse and famous artistic output. Thomas Friedman similarly describes globalization as being spiky and concentrated in big cities. Other regions are comparatively less productive and less studied. Either this reflects museum curators’ historic bias against Africa, Latin America, and the “Global South” in favor of Europe. Or this might reflect a more fundamental historical reality: If geography guides artistic production and privileges regions with good geography, like areas surrounding the Mediterranean, then landlocked and inaccessible regions with poor geography will have less artistic output.
.
.
Art objects from ancient cultures like China, Egypt, and Sumeria frequently have known provenance but unknown year of production. Unfortunately, they are therefore excluded from this visualization. There are many objects in the collections with known provenance but unknown production date. Figure one illustrates objects with known provenance and known year. Figure two shows objects with known provenance only.
.

Figure 1: All art with known provenance AND known year.

Figure 2: All art with known provenance
.
The original data was downloaded here from the Met Museum’s website.
This visualization and interactive map are free to view and download here.

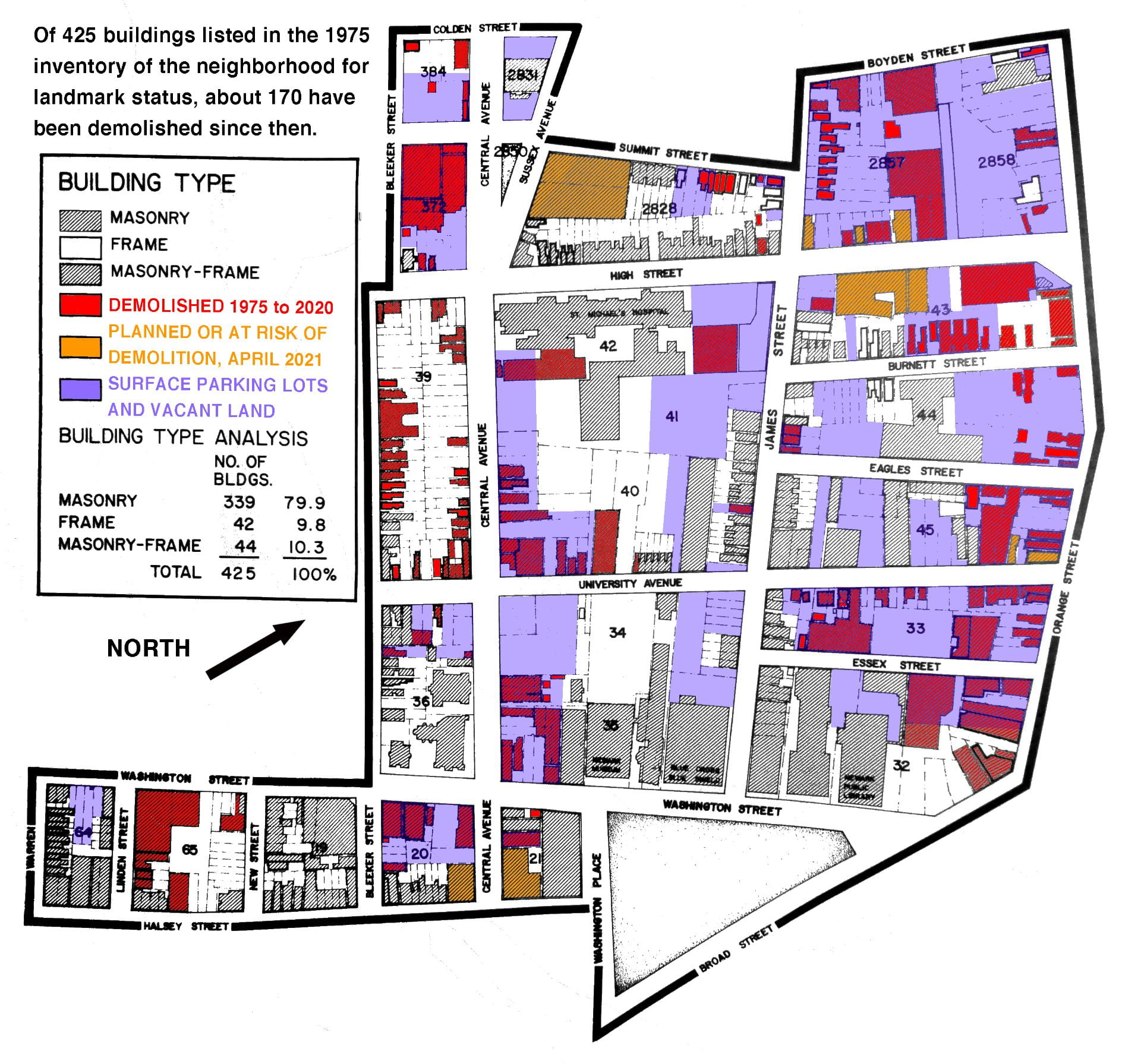
 Explore an interactive map of the 300+ acres of parking in Downtown Newark. This map is part of
Explore an interactive map of the 300+ acres of parking in Downtown Newark. This map is part of